It is block of statements are used to perform the task called as methods.
Writing methods avoid the rewriting same code again and again. Suppose you have block of statements in your program that will calculate sum of two numbers and perform some operation on it. But at later, you want to calculate the sum and average in another program at that time, you need to write the same code again. So it will increase your efforts and time also. If you define one method and write the sum of number logic into it, if you want to calculate same in another program, you can do it by just calling the method. So it will help you to avoid the same code again and again. That’s why methods comes into picture.
Note- Writing all codes into one method that is not good programmer practice.
Syntax-
[Specifiers] return_type method_name (parameter 1, parameter 2,…parameter n)
{
Statement 1
Statement 2
--------------
Statement n
}
Note- Method parameter is an optional thing.
Example-
public class Example {
// int is return type
// getTest is method name
int getTest() {
// return integer value only
return 1;
}
//String is return type
String getDemo() {
//return string value only
return "s";
}
//void is return type
//getData is method name
void getData() {
//no need to return anything
}
}
There are two types of methods as
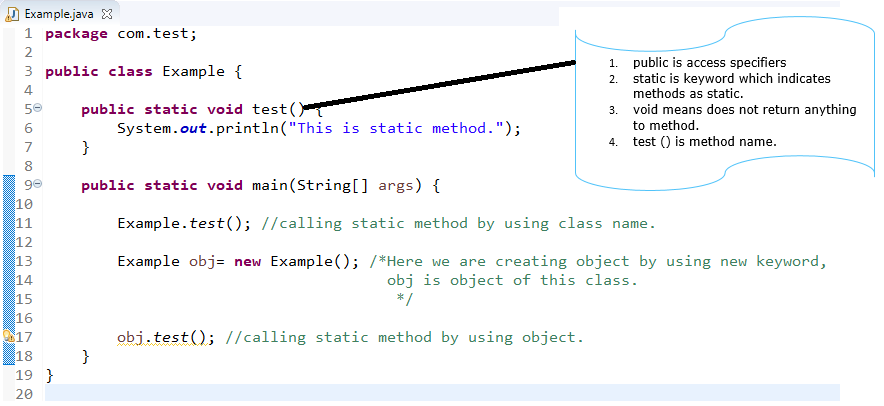
When you define method in class with using static keyword called as static method.
We can call this method by two ways.
First way is by using class name.
Example.test ();
Second way is by creating object of class.
Example example= new Example ();
example.test ();
In same program, we can call it test();
Example
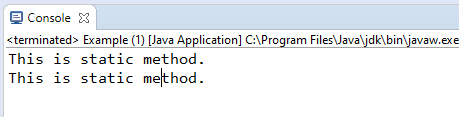
Output
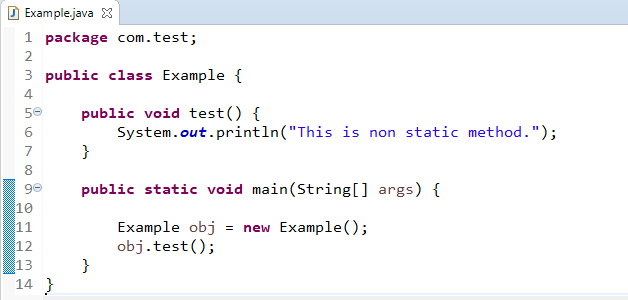
When you define method in class without using static keyword called as non-static method.
We can call this method by creating object of class only.
Example example= new Example ();
example.test ();
Example-
Output
Method with Parameter Concepts
Program for design method as getStudentName() which return the student name.
public class Test {
// Design method which return student name
String getStudentName(String name) { // ram is store into name
return name; //return name to method
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test();
String s = test.getStudentName("ram"); // calling of method
System.out.println("student name>>" + s);
}
}
Output
student name>>ram